Definition
A heart murmur is sound produced by turbulent blood flow, particularly from the heart's valves. They can be found in infants or develop later in life. A heart murmur is often innocent and doesn't require treatment.
Heart Murmur Audio
Stethoscopes are used to listen to heart murmurs. A normal heartbeat sounds like "lub-DUB", which are the sounds of your heart valves closing. This "lub-DUB" sound changes, often with additional sounds being heard.
Heart Murmur Sounds
On this website, we provide lessons, reference guides and quizzes for auscultating heart murmurs. This includes gaining an understanding of cardiac rate and rhythm, conditions of the valves and possible anatomical abnormalities such as congenital defects. Links to our lessons, guides and quizzes are found in the 'Quick Links' box to the left. The remainder for this pages provides an overall listening guide for heart murmurs.
Timing and Cadence
Systolic murmurs occur between the first heart sound (S1) and the second heart sound (S2). Diastolic murmurs occur between S2 and S1. In addition, timing is used to describe when murmurs occur within systole or diastole. For example, early systolic, midsystolic or late systolic. See our courses on Systolic and Diastolic Murmurs for more information including audio recordings, waveforms and animations.
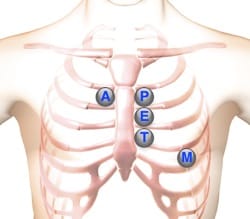
Heart Auscultation Points
Auscultation of the heart is typically performed over five heart auscultation areas on the anterior chest wall. Please refer to the torso illustration for these locations. Use the stethoscope's diaphragm, switching to the bell to hear lower pitched sounds.
 |
Aortic Valve Area | Second right intercostal space (ICS), right sternal border | |
 |
Pulmonic Valve Area | Second left intercostal space (ICS), left sternal border | |
 |
Erb's Point | Third left ICS, left sternal border | |
 |
Tricuspid Valve Area | Fourth left ICS, left sternal border | |
 |
Mitral Valve Area | Fifth ICS, left mid-clavicular line |
Duration
Heart murmur duration refers to the portion of systole or diastole that the murmur occupies. Terms used include short and long. Murmurs lasting throughout systole are referred to as holosystolic or pansystolic.
Pitch
Evaluation of the murmur's pitch should be made by classifying the pitch (frequency) as low, medium or high. The stethoscope's bell can be helpful with low-pitched sounds while the diaphragm is used for medium or high-pitched sounds.
Shape
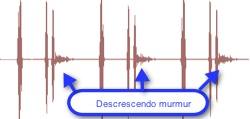
Some murmurs are described by the sound's shape. Common classifications include crescendo (increasing intensity), decrescendo (decreasing intensity), crescendo-decrescendo (increasing then immediate decreasing intensity). Crescendo-decrescendo is also called diamond shaped. Rectangular, also termed plateau indicates a heart murmur of constant intensity. Our lessons include waveforms that illustrate these shapes.

Tonal Quality
Listen for additional aspects of the murmur's sounds. Heart murmurs may have qualities that can be noted as musical, harsh, blowing, booming, sharp or dull.
Respiration and Patient Position
Respiration or patient position can influence murmur intensity as well as heart sound splitting. These factors will be described within the heart sound lessons. Generally speaking, murmurs increasing with expiration originate with left side (aortic or mitral) valves, while murmurs increasing in intensity with inspiration originate with tricuspid or pulmonary valves.
Within each lesson, the author provides an sketch of the patient's position during auscultation, such as supine, left lateral decubitus, squatting or sitting.