Introduction Part 1 ECG Interpretation #314
Introduction
- Cardiac rhythms are typically named by the site of origin or heart structure where the problem is occurring
- These junctional dysrhythmias primarily affect the P wave.
- Electrical impulses formation and flow in a normal heart follow a forward or antegrade flow through the atria. This results in the upright P wave we see with Sinus rhythms.
- With junctional rhythms, the impulse is initiated in the AV junction. This impulse point results in a backward or retrograde flow of electricity during atrial depolarization.
- This change in the flow of electricity results in an inverted P wave. This morphologic feature is unique to Junctional complexes and rhythms.
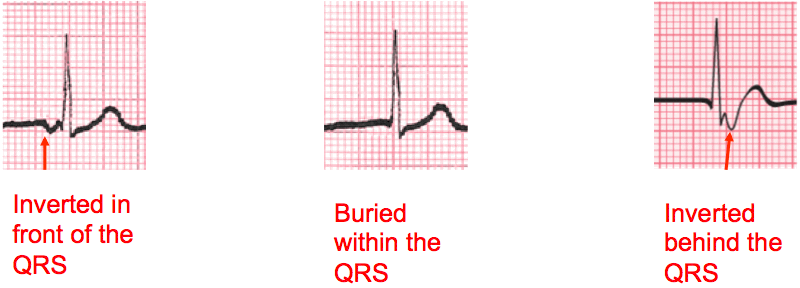
Inverted P Wave
- The result of this retrograde depolarization is the classic inverted P wave.
- Because the electrical impulse causing atrial depolarization may come from anywhere in the AV junction. This can affect the location or coordination with the QRS complex.
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- ECG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- ECG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language ECG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 6th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1265013470, ISBN13: 9781265013479
McGraw Hill, 2023 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
EKG Reference Guide
EKG.Academy -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
-
ECG Reference Guide
PracticalClinicalSkills.com